The geobrowser is a map-based web application, allowing users to perform data exploration, data visualization, data analysis and data processing.
The application spreads on the common OGC standards:
The geobrowser is based on a “current search” concept. The “current search” is an entity representing the data of the catalog we are currently navigating. It is defined on the couple {current opensearch description, current search parameters}:
On the geobrowser, users can change and manipulate the current search in 2 ways:
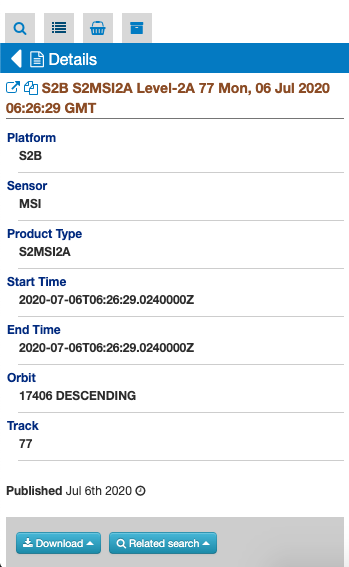
A current search always involves a current search result, which is the search result on the catalog with a specific opensearch description and a specific parameters values set. That result is on OWS context standard, encoded in geoJSON format, and contains a list of results entries called Features. Each feature is shown on the Results Panel, and a details view for a selected feature is offered to show all the features info. Morehover, the features containing geographic information (like bounding box, map image, WMS service) are also visible and represented on the Map Services panel.
Let’s see in the details each component of the geobrowser.
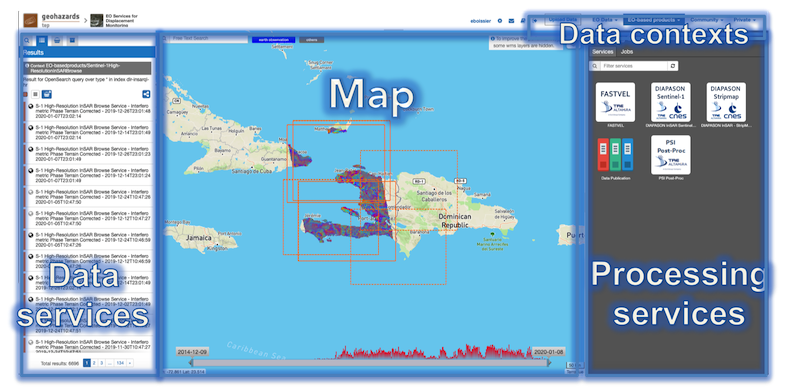
The Geobrowser is composed of:
Map services, the map area;
Contexts menu, a menu used to switch among predefined search;
Data services panel, a panel showing all info about the current search and the saved results. This panel is splitted in more sub panels, shown only one at a time to improve focus and usability:
- Search Panel
- Results Panel
- Features Basket panel (or saved results)
- Data packages panel
- Details panel
Processing services panel
The Map Services panel is a simple geographic map, on which you can zoom in, zoom out, pan and see all the geographic features of the current results. The Map Services panel can show on the map features as:
The Data Services panel shows all information about the current search and the saved results. This panel implements three of the “Information Seeking Mantra” interactions (search, list results, details on demand).
These three interactions are represented in three different views and panels: the search tab, the results tab and the details tab.
Two extra tabs are handling the user saved results and the user defined Data Packages.
To improve focus and usability, one subpanel is visible at a time, via a tab switcher. Users can open or close the Data Services panel via the Tools button.

The search panel is a view containing all search parameters associated to the current catalogue on which the search will be performed. The search panel is shown as a form, and, depending on the opensearch descriptor document, some parameters are just free text, some of them have type restrictions, others can be chosen from a list. Some predefined parameters, if present on the opensearch descriptor, are also visible as an external widget on the map, like the Time slider, the Search terms and the Geo Filters. The startIndex standard parameters is also shown as a pagination widget inside the results panel.
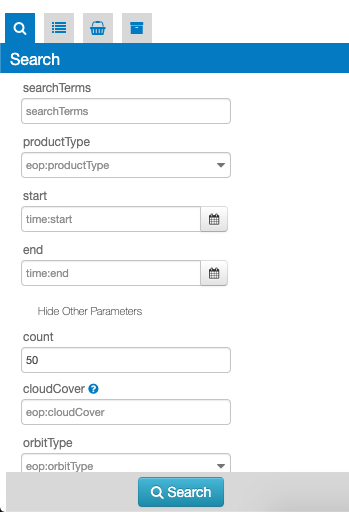
This panel shows the result of the current search as a list of features. Some search results are also visible on the panel header. When a search is done this panel automatically is activated showing the results.
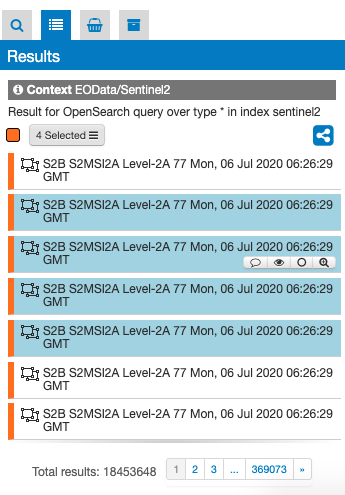
From the results panel users can do different interactions and operations:
Users can save the features from the results panel into a personal user space called Features Basket (or saved results). This panel is similar to the results panel, since it has a list of the features saved by the user and those features are visible in the map and on the details panel, but it could contain features from different catalogs. To put features into the features basket users can simply drag one or more features on the features basket icon.
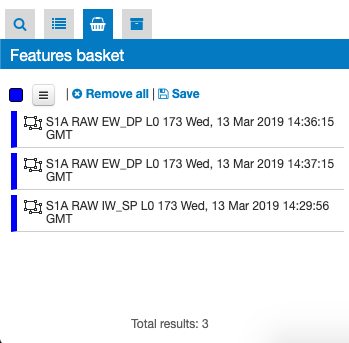
Users can navigate among the features (like on the results panel), remove one or more features or clean all the features in the basket. Moreover users can save and export the features basket in a Data Package, allowing users to share results.
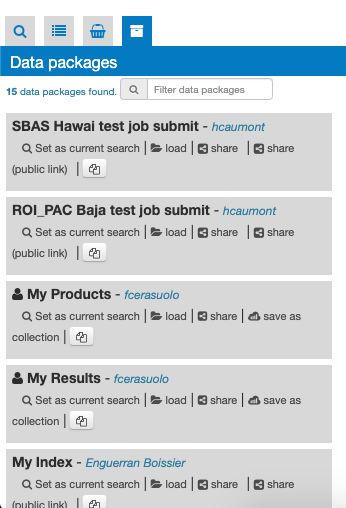
A data package is a saved collection of features. The Data Packages panel shows all data packages visible to users. A data package can be opened by replacing it to the Current Search.
The details panel is a “floating panel”, that is, is a panel not visible as a tab. Users can also see this panel from a specific feature, by double click on it, or by opening the details from the popup. This action shows in a vertical scrollable layout page all description information of the feature, including summary, images, key-value information. Also, from the details panel user can perform some actions, like filter the current search by the feature spatial information, check out some feature correlated results or set some styles options to the relative map feature (if available)
While the Data Services panel allows users to navigate and retrieve information on the data, the Processing Panel allows users to perform operations on the data. The Geobrowser uses WPS standard to provide rules for standardizing inputs and outputs for invoking processing services. From the processing panel users can:
To do this there are 4 views: Services tab, Service Details, Jobs tab, Job Details. For no logged users is only possible to view the jobs information and results.
This tab contains the list of available Processing Services. Users can apply some filters to looking for a specific service. Choosing a service the relative details are shown.
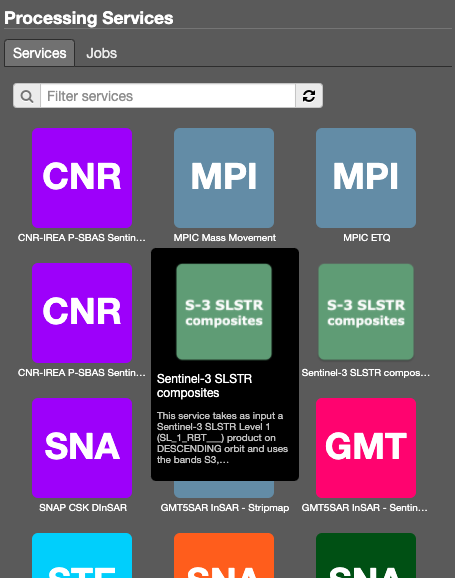
This view includes a description of the selected service (title, version, description, and so on), followed by a form of all service inputs. Users can fill the form manually, by features dragging (if available for the input) or by the geobrowser clipboard. Is also possible to import and export parameters set in a json format.
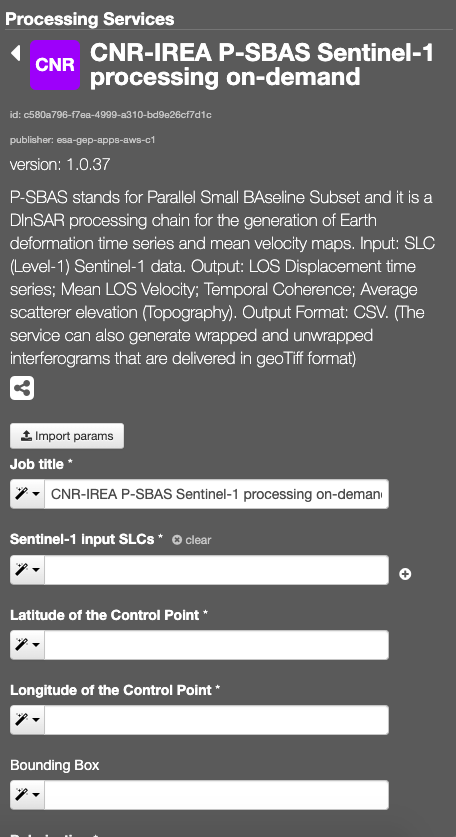
This tab contains the list of available jobs associated to the user or thematic app. Users can filter the job for job title or job type (mine, thematic, all). Details on jobs can be accessed by clicking on the title of the job. For running jobs it’s possible to view the running percentage status.
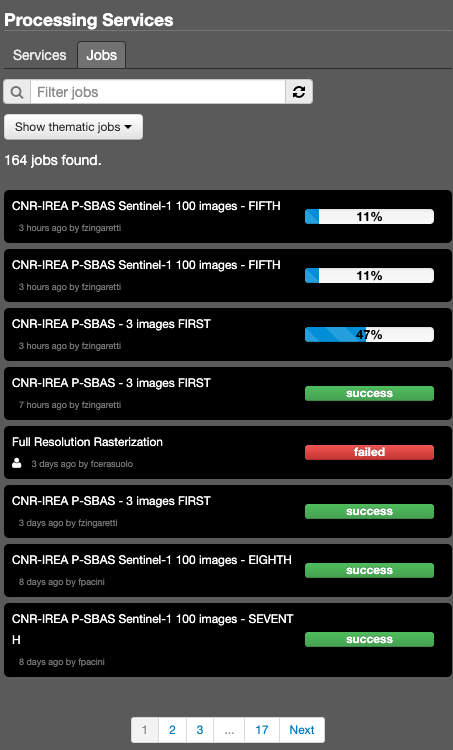
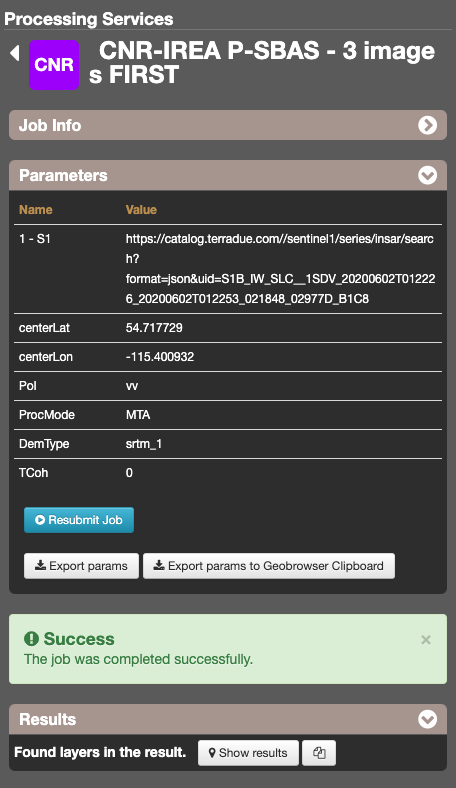
The job details view contains all job information, like some service info, job time, job author, job status (running, succeeded, failed) and job results. A job result can be represented as a Opensearch Description element, so users can see the results of a job on the Map Services panel and on the Catalogue control by changing the Geobrowser Current Search with the job result. It’s also possible to resubmit the job with the same parameters.
To simplify the user view on the map, all the map tools buttons are hidden. To show them, simply move the mouse cursor to the left side of the map.
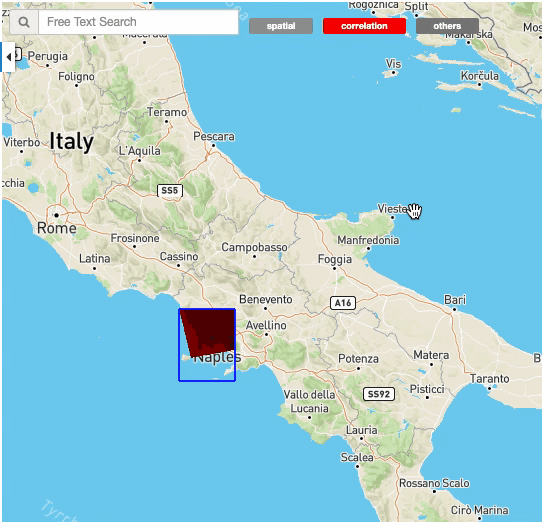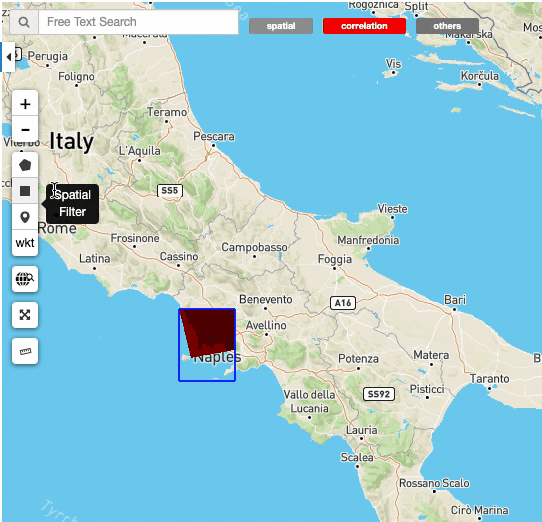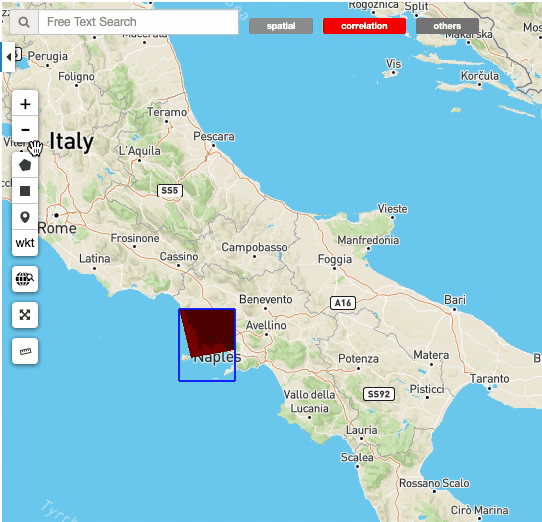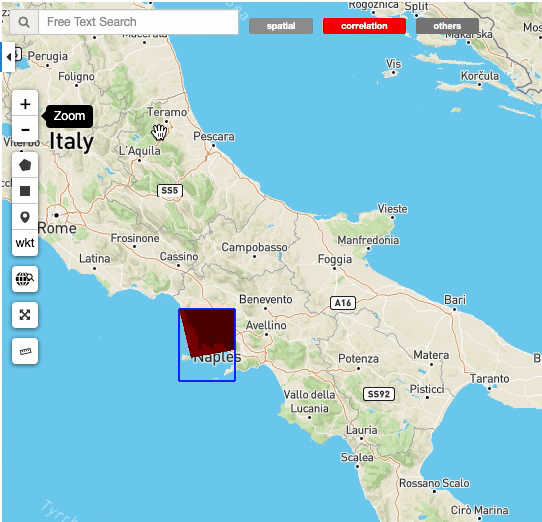
Some Opensearch Descriptions have special standard parameters, for some of them the Geobrowser has a set of widget to allows users to easily and visually change the parameter values. For example, the geo:box parameter (filter by rectangle) and the geo:geometry parameter (filter by a custom shape in wkt) have some spatial buttons inside the map tools. From these controls, users can directly draw on the map the shape to perform the spatial query.
 Edit the search bbox by drawing a polygon on the map
Edit the search bbox by drawing a polygon on the map Edit the search bbox by drawing a rectangle on the map
Edit the search bbox by drawing a rectangle on the map Edit the search bbox by selecting a point as AOI
Edit the search bbox by selecting a point as AOI Allow to enter a WKT or upload a shapefile, a kml or a geojson to be displayed on the map as bounding box
Allow to enter a WKT or upload a shapefile, a kml or a geojson to be displayed on the map as bounding boxThe Geocoding control allows users to: - find some places on the map (giving a place text); - perform a spatial query on the data by a place found. A place text could be a country, a city name, a street, a mountain, a river, and so on.
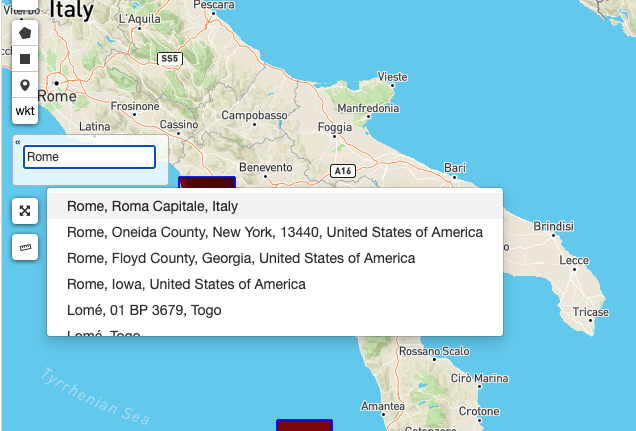
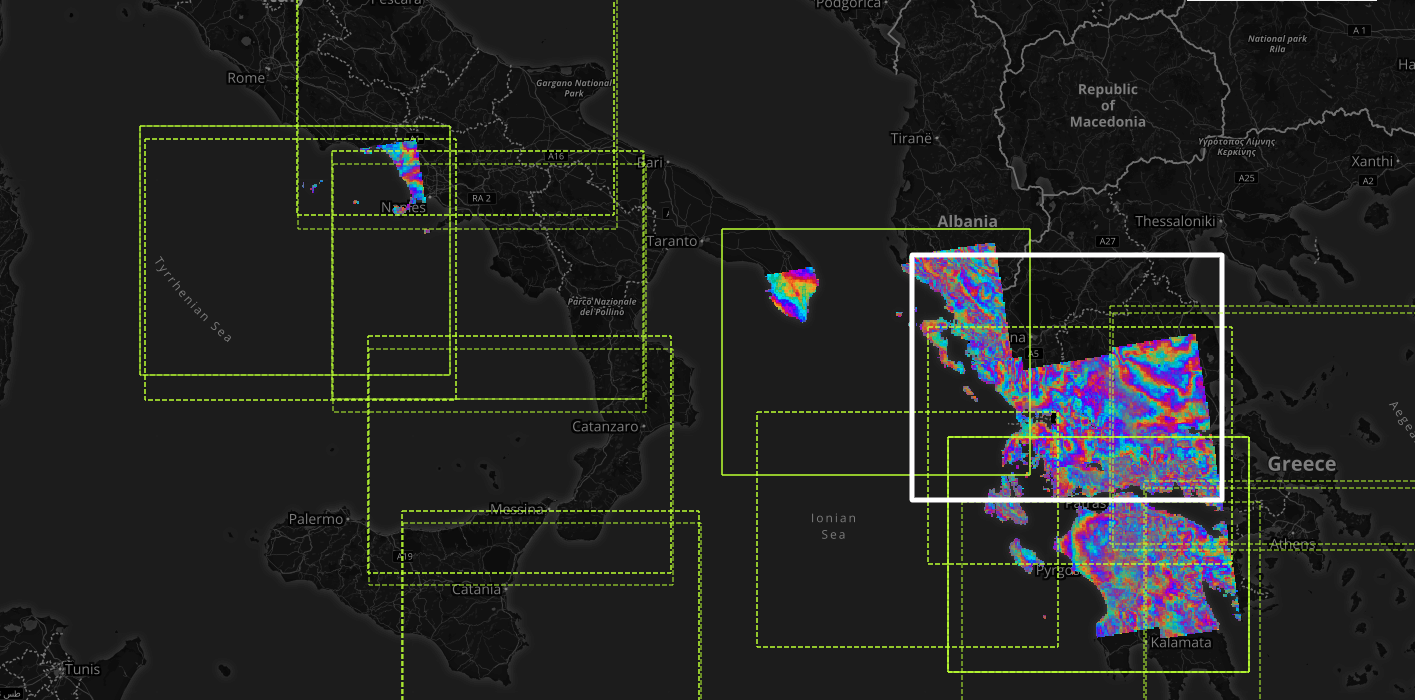
The geobrowser can show multiple WMS (Web Map Service) layers if there are features exposing WMS layer information on the current search result. In order to improve the performance and the User experience, when an EO Collection exposes WMS layers, some of them can be active whereas others can be hidden. This behaviour happens after a certain level of zoom, moreover the actual number of the active layers is dynamic and depends on the number of WMS requests necessary to show the layers on the current view on the map. A User can interactively choose to see a hidden layer, by clicking on it on the Results Panel or directly on its footprint on the map. Footprints are indeed always visible on the map. Furthermore, a User can decide to “lock” one or more layers to study, for instance, correlations between them. Here below, a legend shows the possible statuses for a product in the result table:

On the map, products containing active/hidden WMS layers differ as shown:
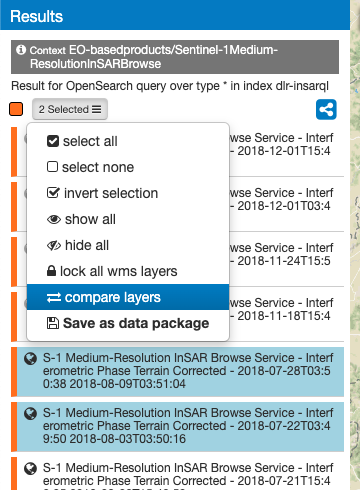
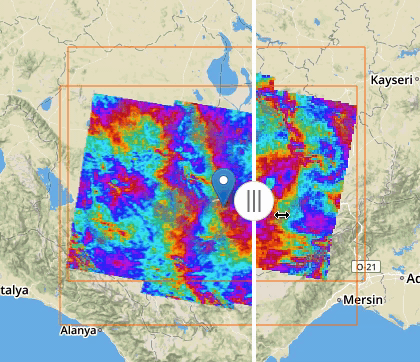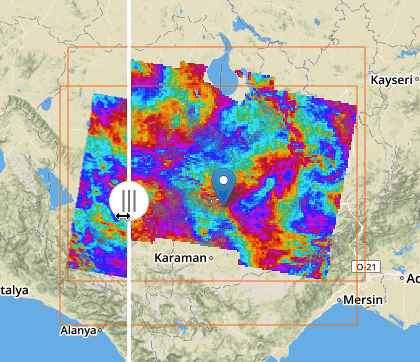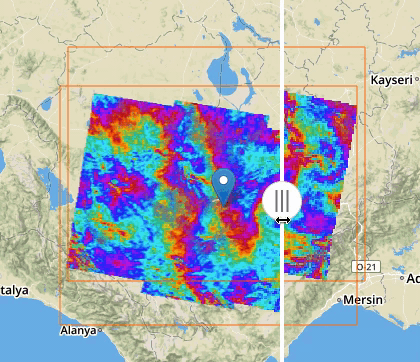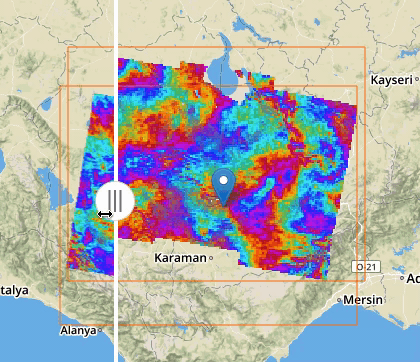
If two or more features exposing WMS are selected, a new menu item is added on the features selecting dropdown menu: the “Compare Layers” button. By pressing this button an interactive visual comparing tool is opened, showing only the selected layers with a vertical slidebar. This tool is useful for juxtaposed wms layers to allow easy comparison and detection of changes.
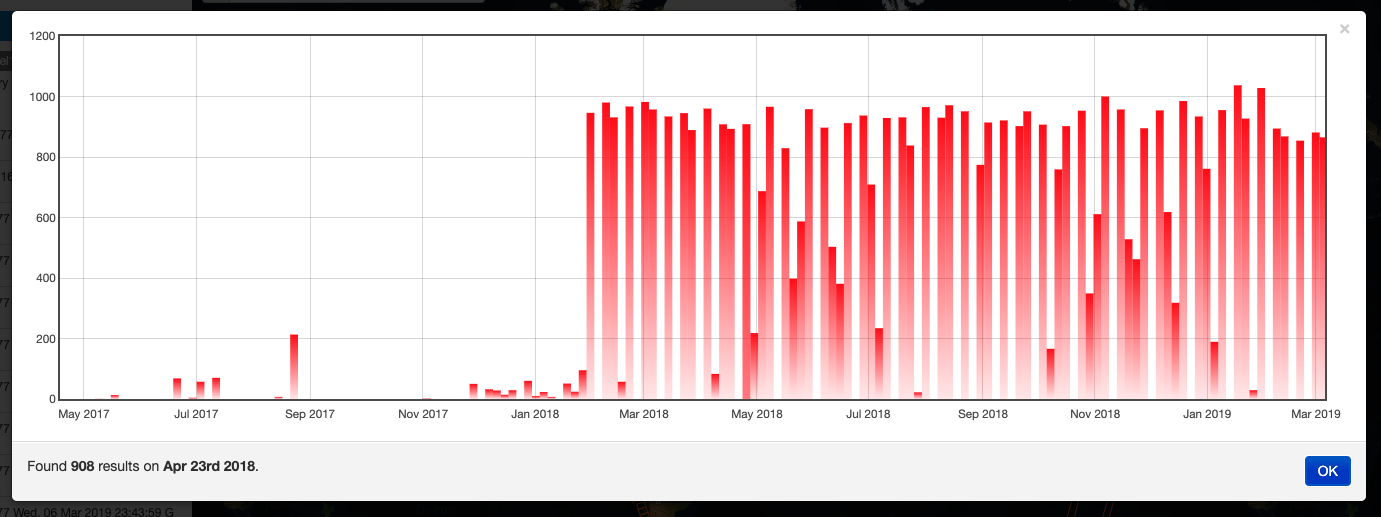
If the Current Opensearch Description exposes the standard temporal query parameters (time:start, time:end), and if the thematic app allows it, a Time Slider is added on the bottom of the map. This widget is useful to visually select a time range for a time restriction on the current search. Moreover, the Time Slider contains visual representation of the data distribution over the time.

The Search Terms is a default standard Opensearch Parameter. The geobrowser represents this with a simple input text widget, always visible on the top left of the map. It’s a “keypress” triggered input, users don’t need to press a confirmation after typing, the search is automatically launched as users stop to type the text to search.

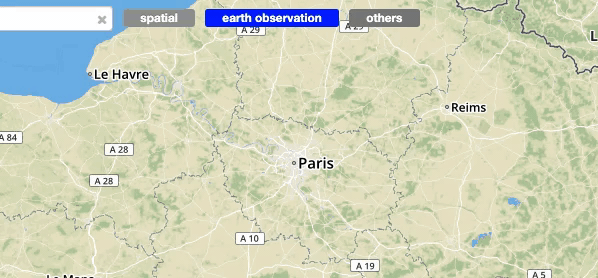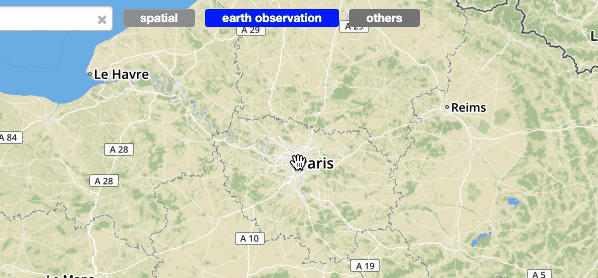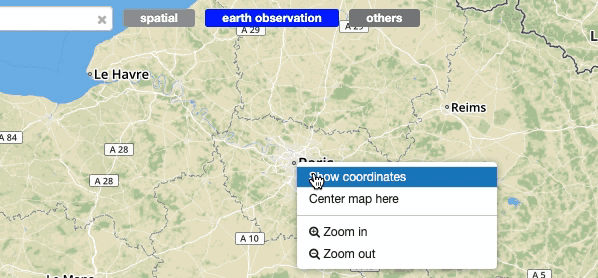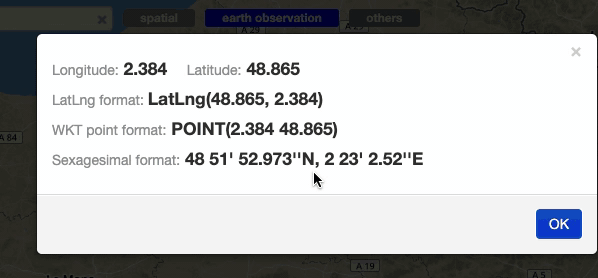
With a right-click on an empty point on the map a context menu will open to show some actions like “Center map here” (pan in the selected zone on the map), zoom in, zoom out, and a useful utils “Show coordinates”. This utils will show a popup with information about the coordinates of the point selected on the map, in different formats.
On the top-right of the map there’s the layers control: collapsed in a button, by going over it a panel will expand, showing the list of all layers and layers groups in a scrollable panel.
There are two types of layers:
From the layers control users can switch between the base layers (defined on the thematic app configuration), and can show/hide the overlay layers. On the geobrowser there are some predefined overlay layers:
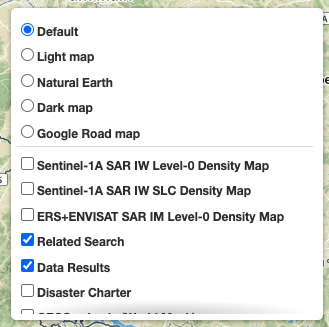
Moreover, users can also set the opacity by clicking on the opacity button and set the opacity slider.
The geobrowser clipboard is a facility used to pass data between the geobrowser components, in particular from the current search status and results to the WPS services fields. The Geobrowser Clipboard consists in a set of adaptable and dynamic information stored in a temporary buffer during the user interaction. For example, if the user selects one or more features, some selected feature information (such as start time or identifier) are stored in the clipboard for a reuse of the values. Another clipboard type can be a search value, like search start date or end date.
Each clipboard element has a identifier, a value, a clipboard type (feature or search) and a data type. A value could be an array, for example, if the user selects 10 fields, the search:startDate geobrowser clipboard item stores 10 start dates.
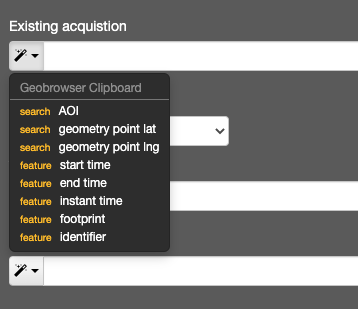
The WPS service field has a clipboard menu, used to retrieve the clipboard values previously stored.
A feature (or a set of features) selected from the Results Panel can be dragged to use it as a WPS service parameter value, or to add it to the features basket. For the first operation it’s necessary to have the WPS service opened with the allowed target WPS field parameter visible, simply by dropping the feature(s) on the WPS field, this field will be set with the feature identifier. This operation is available for the features basket result too: it’s possible to add a feature from the features basket on a WPS field parameter. For the second operation (add to features basket), users can add selected features from the results panel to the features basket panel simply by dragging the features and dropping them into the features basket tab icon.
All features containing geographic information are always represented on the map as geometric shape (like a rectangle, a point, a polygon and so on). Moreover, some of these “spatial features” also contain raster data, like images or WMS tiles. For these features there are some visualization function, located on the Details Panel of the selected feature (by doing double click on a raster feature from the results panel). These function are visible as an expandible section called “Raster visualitazion functions”.
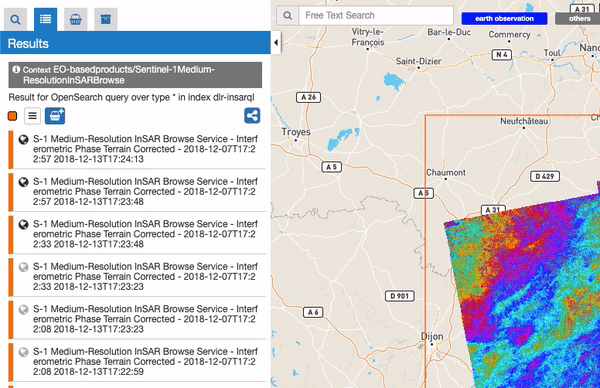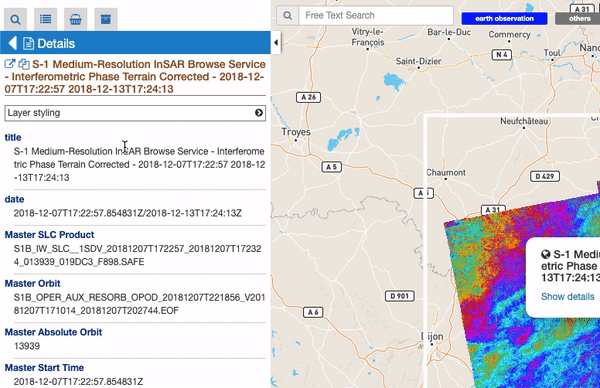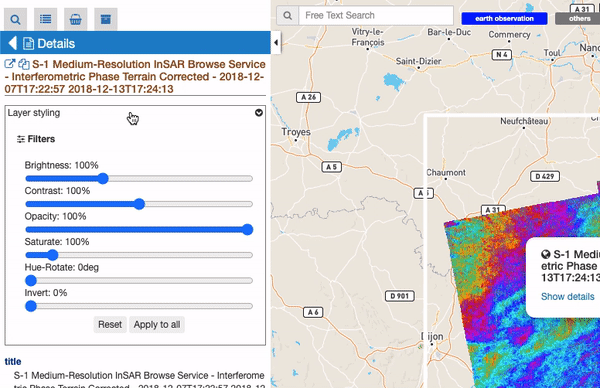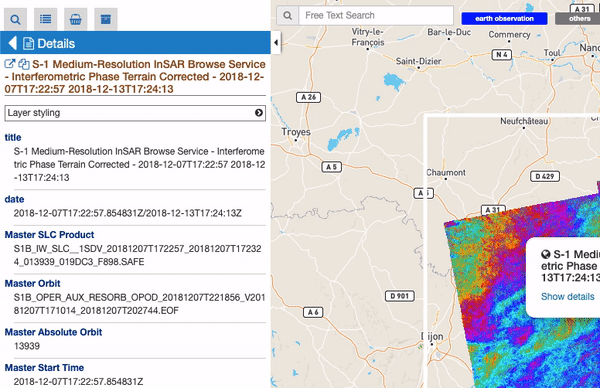
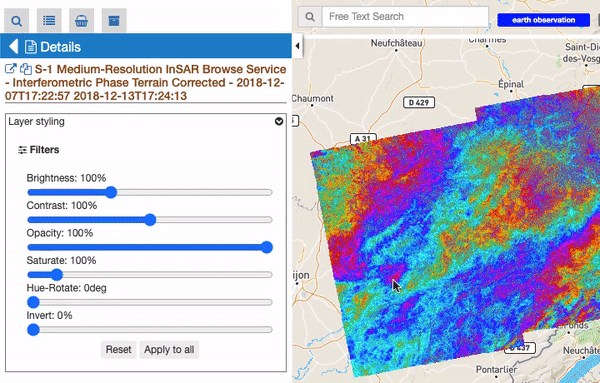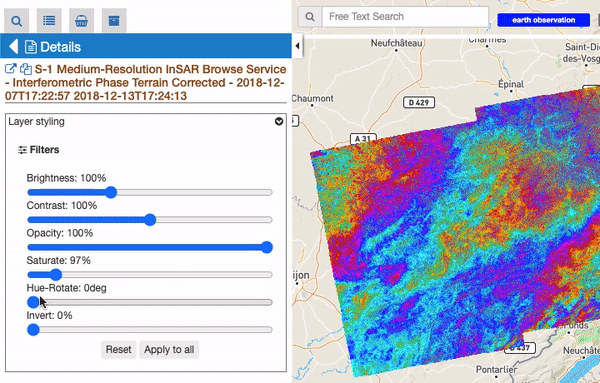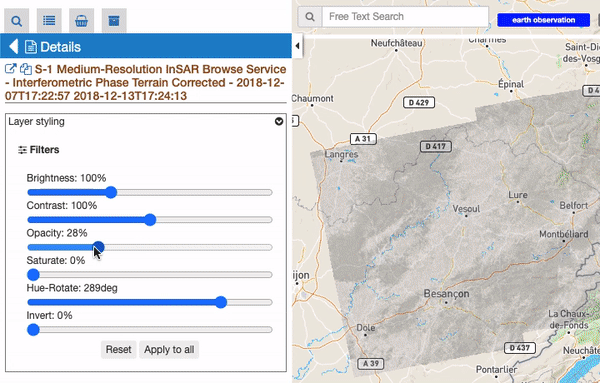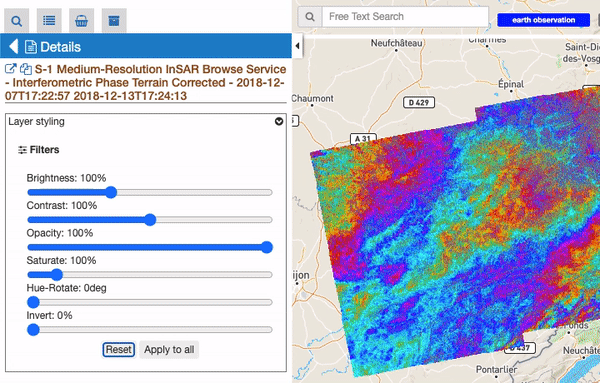
For all raster features (all features containing raster data) there is always a subsection called “Filters”, including some customizable graphical settings, like brightness, contrast, opacity, saturation, and so on. The changing of these filters is immediately visible, and the settings are saved for current session. Users can reset the filters to the default value and can also choose to apply the settings for a feature to all visible raster features.
An additional subsection called “WMS Styles” can be visible for raster features represented by a WMS service (this is the case for most of the processing results on the GEP). Users can switch among a set of available WMS styles pre-loaded by the operator in the user workspace. By clicking on a WMS style icon, the style is applied to the selected WMS feature and for all similar features.
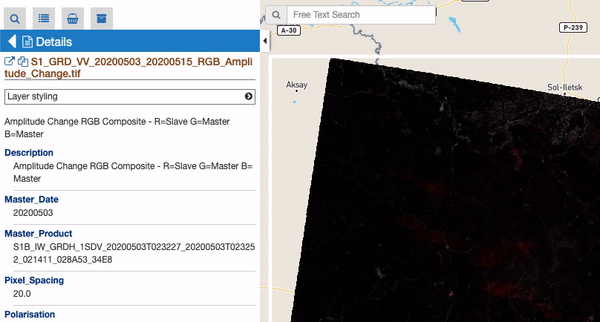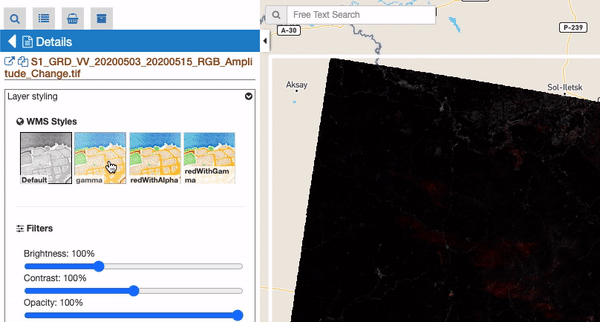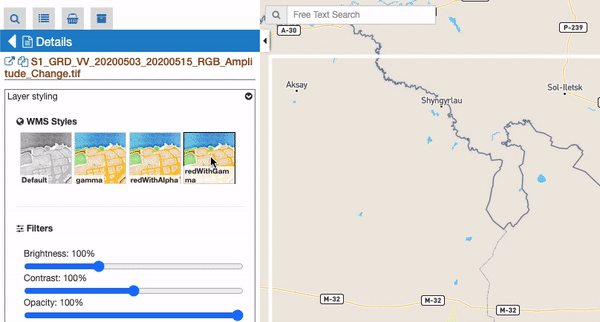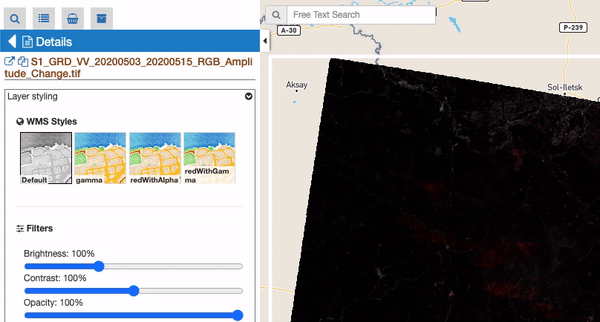
Notice: This subsection is only visible if there is at least one WMS style associated to user’s workspace. WMS styles are loaded by the operator upon user request and have to be provided in the standard OGC Styled Layer Descriptor format. Examples can be found here: https://docs.geoserver.org/stable/en/user/styling/sld/reference/rastersymbolizer.html and https://docs.geoserver.org/stable/en/user/styling/sld/cookbook/rasters.html . See https://docs.geoserver.org/stable/en/user/styling/index.html for further information about WMS Styles.
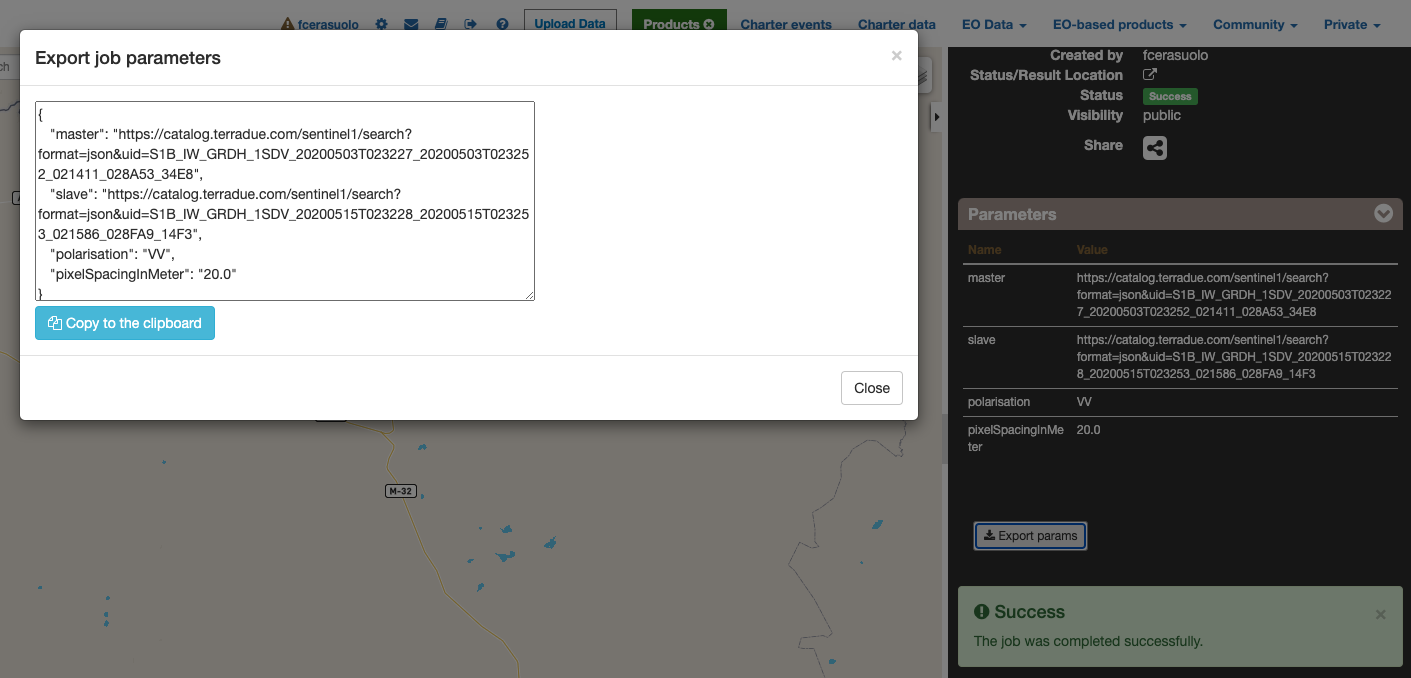
When users select a WPS process to execute, they can set all parameters by filling the relative form. However, in some cases can be useful to set (or to get) all parameters in a single block structure. In this way users can prepare the wps parameters in an external application (like a text editor), or they can take the wps parameter of an existent wps Job, to create a new WPS job with the same or a portion of the same paramaters. To perform this there are 2 utilities: import and export parameters. On the WPS process description (and form) there is a “Import Parameters” button. Once clicked, a popup form with a JSON structure (auto filled with sample values to help users) in the textarea of the form. The JSON is a simple key-value pairs object, with single string value for single parameters, and array of strings values for multiple parameters. After filling the textarea, by pressing the “import button” the popup is closed and all WMS form parameters are filled by matching the parameters set in the specified JSON.
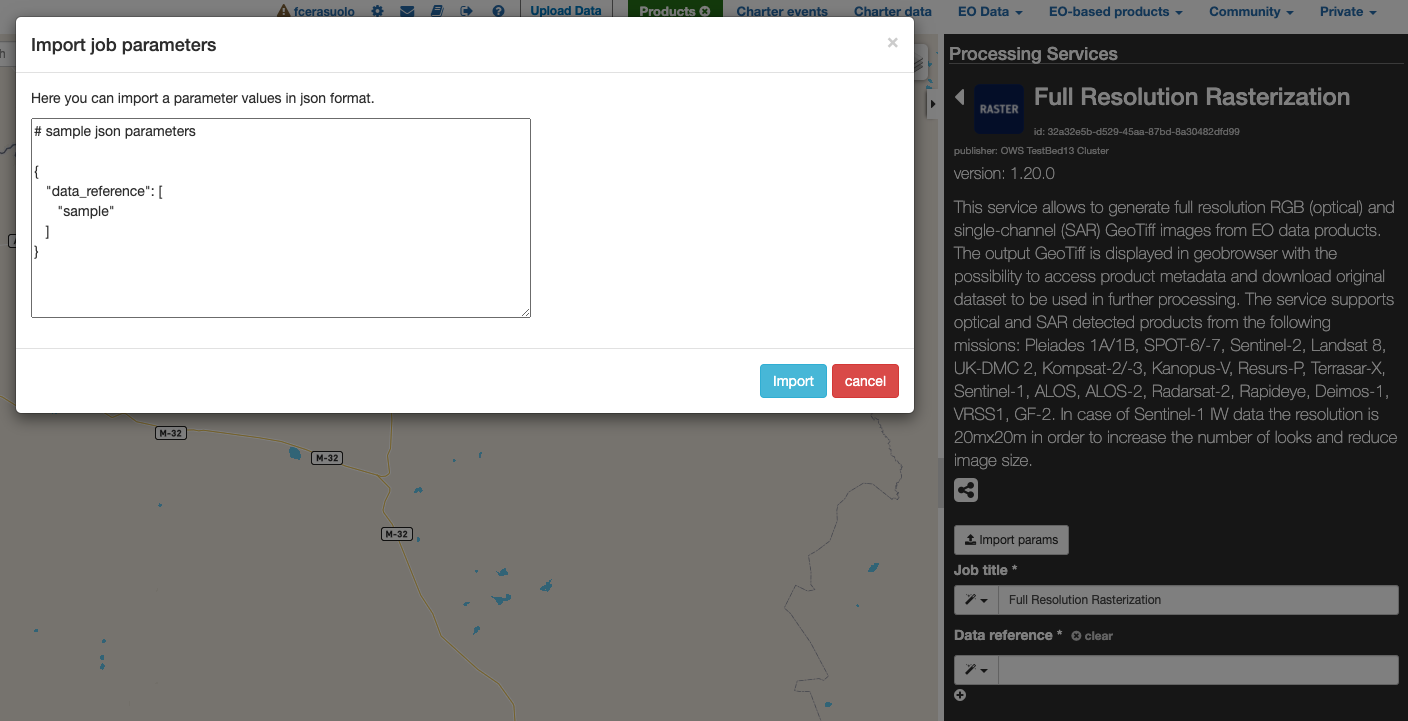
On the WPS job description under the parameter values list there is a “Export Parameters” button. Once clicked a popup is opened, showing in a text area the JSON representing all WPS parameters set for the selected job. Users can copy this JSON in the clipboard, for example to change some parameter values and re-import these parameters in a new WPS job.